정보통신분야 기술사 훑어보기
- 정보통신분야 기술사 훑어보기
- 정보통신분야 기술사 출제기준
- 기술사: IT경영
- 기술사: 융합 IT
- 기술사: 프로젝트관리
- 기술사: 소프트웨어 공학
- 기술사: 정보보안
- 기술사: 데이터베이스
- 기술사: 네트워크
- 기술사: 알고리즘
- 기술사: 에세이
종류
- 정보관리기술사: Professional Engineer Information Management
- 기존 정보처리기술사
- 합격률 2022 5.2% 2021 8.8% 2020 7.1%
- 컴퓨터시스템응용기술사: Professional Engineer Computer System Application
- 기존 전자계산조직응용기술사
- 합격률 2022 12.5% 2021 11.9% 2020 18%
- 네트워크, 클라우드, 시스템 엔지니어면 컴퓨터시스템응용기술사, 나머진 정보관리기술사로.
- 기술사법으로 관리된다.
시험 관련
출제경향
- 60%는 거의 그대로 출제, 나머지 20%는 비슷한 유형 출제
- 총 80%가 기출 변형
- 시험관이 그때 그때마다 차출되고 해당 시점에 내고 싶은 문제를 내기 때문에 범위 예상이 힘들다.
- 기술 트랜드나 IT정책을 팔로잉하고 있어야한다.
준비물
- 1.6mm 펜 4자루 이상: 큰 글씨 선호
- 파일럿, 빅 볼펜이 볼펜똥이 안나옴.
- Pilot Super Grip G
- BIC Cristal
- Dong-A AnyBall
- Zebra Tapli Clip
- 모양자: 플로우차트 그리는데 필요
출제위원
- 출제위원은 3명, 그 답안을 가지고 다른 사람 3명이 체점을 한다.
- 1교시 문제를 받자마자 교수, SI기술사, 공무원기술사일지 파악해야한다.
- 교수: 학구적 스타일
- SI기술사: 프로젝트를 해봤는데 이슈있는 스타일
- 공무원기술사: 공공, 법 스타일
- 이걸 파악해서 연관된 서브노트를 쉬는 시간에 본다.
- 평소 5년치 분석할 때에도 이런 관점에서 분석해야한다.
느낌
- 회사에서 했었던 업무들에 대한 프레임워크들을 문서로 리뷰하는 느낌이였다.
- 이 시험은 기사처럼 암기로 되는 시험이 아니다. IT기법이 왜 그렇게 발전해왔는지, 그걸로 기업의 비지니스에 IT가 어떻게 기여했는지 산업 전반을 이해해야 답을 할 수 있다.
- 라이팅 문제처럼 에세이를 써야하고, 면접을 대비하는 것처럼 나만의 답안들을 만들어야한다.
- 장기 말에서 장기를 두는 사람을 만드는 시험이랄까.. 중인 중에서는 제일 높은 관직이지 않을까..
- 사람들을 설득하는 포지션이기에 질문에 대한 답변을 말로, 손으로, 다이어그램으로 설명할 수 있게 많이 연습해야할 것 같다.
- 손으로 작성하는게 생각보다 쉽지 않다.
- 시험의 70%가 공공 분야와 관련이 있다.
- KoreaScience의 자료가 좋다.
과정
- 1,000 시간을 투자하면 얼추 합격한다고 한다. 9시간 투자시 4달, 보통 빨라야 6달이 걸린다.
- 토픽마다 컴포넌트 맵을 작성해야한다.
- 정의, 필요성/목적, 배경/특징/주요 유형, 개념구성/기술구성 그림, 개념구성/기술구성 내용, 구현절차/방법론, 비교 사례/활성화/전략, 구현절차/방법론, 기대효과/발전제언
- 토픽 이론 학습
- 서브노트를 안 쓰고 합격한 사람은 없다.
- 합격한 사람의 한 달 전 서브노트로 쓰는게 좋다.
- 한 번 포맷이 머리 속에 있으면 모든 주제에 대해 해당 포맷을 사용할 수 있다.
- 아는 걸 쓰지말고 물어본 걸 써라. 이건 목차를 잘 만들어야한다.
- 이해한 걸 중심으로 서브노트를 만들고, 1시간마다 8회 반복하면 6개월 이상 암기된다. 외우는 범위를 형광펜을 칠하며 줄여간다.
- 10가지 과목 중에 6개는 80%, 4개는 20%의 에너지로 공부해야한다. 그 중 2개는 강의할 정도로 들여다봐야한다.
- 매번 나오는 것들, 공학적인 기본기는 반드시 알아야한다. 거져주는 문제들이고, 1년에 3번 중 한 번은 이런 문제들을 잡을 기회가 온다.
국제기술사
- 기술사상호인정 협정(MRA) 따라 가능하긴한데 미국은
1년간 미국 근무 경력 또는 비슷한 경력를 요구하여 실질적으로 전환하는 케이스는 드물다. - 국제 기술사는 컴퓨터 관련 과를 졸업해야만 인정이 가능하다.
공부방법
5W1H 개념, 배경, 특징, 방향 나열한 것을 묶는 연습 -> 다시 늘리는 연습 자크만 프레임워크 / 싸이클론 모델
- 개념적 What: 무엇인가 핵심, 원리, 가치, 결어 (기술, 서비스, 절차 중 하나)
- Why: 왜 필요한가
- 구체적 What: 세부구성은 무엇인가 아키텍쳐, 구성도 (개념도), 구성요소 (소스, 매커니즘, 결과)
- How: 어떻게 구현하는가 Provider, Consumer 관점, 이전에는 뭐가 있었는지
- Who: 누가 찾고, 활용하는가
- 결론: 향후방안, 예상 이슈, 발전 방향
예시: ML
- 개념적 What
- 핵심
- 기계
- 학습
- 지도
- 비지도
- 강화
- 데이터
- 원리: 기계가 많은 데이터를 지도, 비지도, 강화학습을 통해 학습하여
- 가치: 사람 대신 판단하여 의사결정을 지원하는
- 결어: 기술
- 핵심
- Why
- 비용절감
- 자동화
- 편의성 (의사결정)
- 생산성 증가
- 품질 증가
- 구체적 What
- 아키텍쳐
- 학습데이터 -> 지도/비지도/강화 -> 대시보드, 자동화도구
- 아키텍쳐
- How
- 동작원리
- 절차
- 적용방법
- Who
- 개인 Personal Assistant
- 기업
- 의사결정
- 고객관리
- 마케팅
- 생산
- 공공 서비스
- 교통
- 안전
- 환경
- 향후방향
- 예상이슈
- 편향적 판단
- 적대적 공격
- 검증
- 발전방향
- 예상이슈
예시: 개념도
입력(사용자) / 프로세싱(플랫폼, 기술) / 출력(서비스)
<---------><------------------><--------->
자크만 프레임워크
| - | 경영진 | 관리자/직원 | 개발자/고객 | 운영자/통제자 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 누가 | - | - | - | - |
| 언제 | - | - | - | - |
| 어디서 | - | - | - | - |
| 무엇을 | - | - | - | - |
| 어떻게 | - | - | - | - |
싸이클론 모델
RTE 를 만들기 위한 비지니스 + 기술 리더의 자세로 토픽을 고민해야한다.
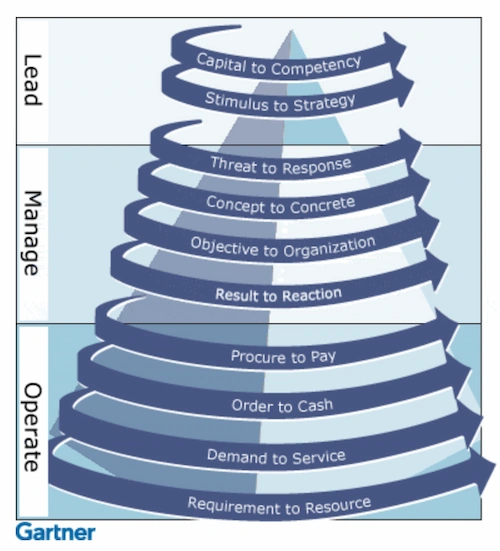
- Lead: 기술사
- Manage: 관리자
- Operation: 개발자
토픽별 전략
보안 토픽
- 리스크 -> 결과 -> 더 많은 대응책
- ISMS 목차를 외우면 대부분의 보안문제를 풀 수 있다.
거버넌스 토픽
- 전략 -> 가치 -> 위험 -> 자원관리 -> 성과관리
융합IT 토픽
- 원칙 문제들은 나의 의견과 응용 포인트를 결론에다가 달아줘야한다.
- 국가: 법 제도 정비
- 서비스제공자: 개선 포인트
- 사용자: 자세, 기준
- IaaS / SaaS 표준 (+PaaS) / SaaS 간편 / DaaS
- 코로나 / 재택근무 도입으로 인한 DaaS의 중요성 대두